SpringBoot之两种配置文件application.properties与application.yml文件的区别及读取方式
为什么会使用properties文件
在软件开发的过程中,会经常遇到一些配置说是需要切换的,例如数据库的配置地址,用户名和密码,可以选择在常量中进行配置,但是当下次需要修改时,则需要将Java代码进行重新编译,再重启服务器。这样导致很繁琐。properties文件的出现使得后期项目的维护中,修改配置时会变得很简单。
yml后缀的又是什么文件
百度百科:YML文件格式是YAML (YAML Aint Markup Language)编写的文件格式,YAML是一种直观的能够被电脑识别的的数据数据序列化格式,并且容易被人类阅读,容易和脚本语言交互的,可以被支持YAML库的不同的编程语言程序导入,比如: C/C++, Ruby, Python, Java, Perl, C#, PHP等,它是类似于标准通用标记语言的子集XML的数据描述语言,语法比XML简单很多。
SpringBoot启动加载配置文件机制
SpringBoot启动时,会默认去寻找开发人员配置的application.properties文件或者application.yml文件来读取配置,其实yml和properties文件是一样的原理,且一个项目上要么yml或者properties,二选一的存在。
1.application.properties的配置方式,类似键值对的存在
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| #数据库连接池配置
spring.datasource.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.datasource.platform=mysql
#配置数据源
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/yang
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=123456
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
#Mybatis配置
#扫描的实体的包
mybatis.typeAliasesPackage=com.yang.bean
#扫描的配置文件地址
mybatis.mapperLocations=classpath:mapper/*.xml
mybatis.configLocation=classpath:mybatis-config.xml
server.port=8088
#自定义信息
userInfo.name=yang
userInfo.pass=123456
|
2.application.yml的配置方式如下,每一个等级占一行,子级别与父级别多一个tab,以此类推,每一个最终节点,配置信息时,冒号后面需要加空格,值得注意的是,一个级别在一个配置文件中只能出现以一次,如果出现多个,则SpringBoot启动的时候就会报错,例如,spring在全局中只能出现一次
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
spring:
datasource:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
platform: mysql
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/yang
username: root
password: 123456
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
mybatis:
typeAliasesPackage:com.yang.bean
mapperLocations:classpath:mapper/*.xml
configLocationclasspath:mybatis-config.xml
server:
port:8088
userInfo:
name: yang
pass: 123456
|
properties文件的读取方式
properties文件读取不需要导入其他的jar包依赖,可以直接使用SpringBoot携带的注解即可
application.properties文件读取某个文件到变量中方法(@Value注解方式)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| package com.yang.controller;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.github.pagehelper.PageInfo;
import com.yang.bean.ResultObject;
import com.yang.bean.User;
import com.yang.service.IUserService;
@RestController
public class UserController {
@Value("${userInfo.name}")
private String name;
@Autowired
private IUserService userService;
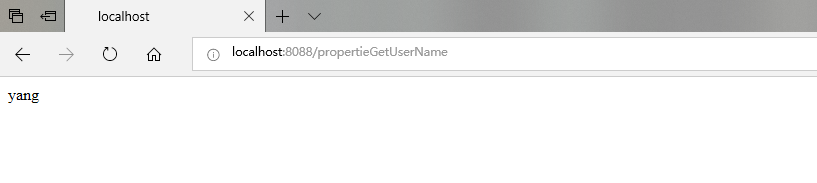
@RequestMapping("/propertieGetUserName")
public String propertieGetUserName() {
return name;
}
}
|
yml文件的读取方式
2.application.yml文件读取配置到某个对象中(@ConfigurationProperties注解方式),注意:对象名与配置文件中名字保持一致,这个方法同样适合properties文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| package com.yang.bean;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "userInfo")
public class UserInfo {
private String name;
private String pass;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getPass() {
return pass;
}
public void setPass(String pass) {
this.pass = pass;
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| package com.yang.controller;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.github.pagehelper.PageInfo;
import com.yang.bean.ResultObject;
import com.yang.bean.User;
import com.yang.bean.UserInfo;
import com.yang.service.IUserService;
@RestController
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserInfo userInfo;
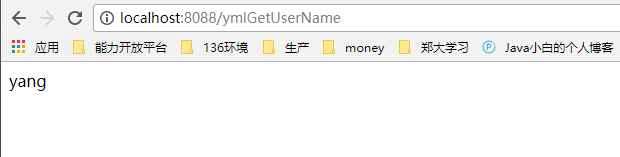
@RequestMapping("/ymlGetUserName")
public String ymlGetUserName() {
return userInfo.getName();
}
}
|
总结及下载地址
本文介绍了properties文件和yml文件两种配置文件的读取的方式,以及SpringBoot如何读取文件中的配置信息,欢迎技术交流 项目源码下载地址(点击我下载,小心你的鼠标)






